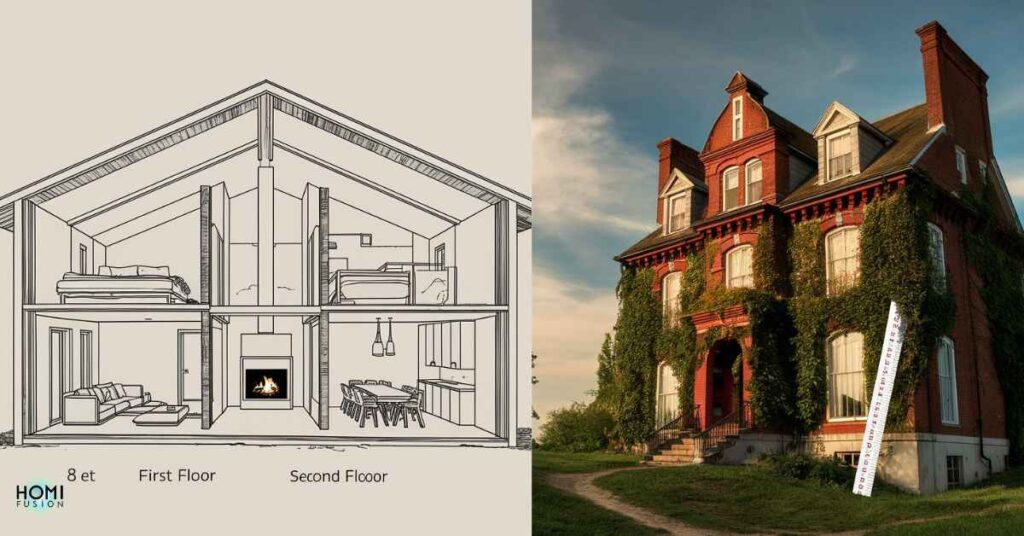
A two-storey house typically stands between 18 to 25 feet tall, depending on factors like ceiling height and architectural style. Building codes and customization options influence this height, alongside considerations of foundation design and roof structure. Location, sustainability and lifestyle also impact height decisions.
Why Do You Need a Two Storey House?
People may prefer a two-storey house for various reasons. Firstly, it offers more living space without requiring a larger footprint, making it suitable for smaller lots. This design also provides better separation of living and sleeping areas, enhancing privacy and reducing noise disturbances.
A two-storey layout accommodates growing families with separate zones for activities. For instance, bedrooms are often upstairs, while common areas are downstairs. Two-story homes often boast a grand appearance and improved views, especially in scenic areas.
Their aesthetic appeal is enhanced by the surrounding landscape. Some homeowners appreciate the opportunity to have a basement or additional storage space below ground level, which is more feasible in a two-storey structure.
What Does a Storey Measure?

- A storey measures the vertical space between two floors in a building.
- It typically includes the floor structure, ceiling and any intermediary space.
- The height of a storey varies depending on factors like ceiling height and construction norms.
- In residential buildings, a standard storey height ranges from 8 to 10 feet.
- Commercial buildings may have taller storeys, often ranging from 10 to 14 feet.
- The total number of storeys determines the overall height of a building.
How Tall Is a TWO Storey House With a Roof?
The height of a two-storey house with a roof is influenced by multiple factors. These include architectural design, ceiling height, roof pitch, and floor thickness. A general estimate for the height of a standard two-storey house with a pitched roof is typically between 20 to 30 feet.
What Shapes the Height of a two storey House?
The information is given below about, how can a two-storey house be shaped by climate effects in different regions:
Cold Climate Regions:
Insulation Requirements: Thicker walls for insulation can increase height.
Roof Design: Steeper roofs for snow shedding may add to the overall height.
Basement Considerations: Deeper basements for protection against frost can impact height.
Hot Climate Regions:
Ventilation Needs: Taller ceilings for better air circulation and cooling.
Sun Protection: Overhangs or shading elements may affect roof height.
Foundation Depth: Considerations for heat transfer may influence foundation depth and thus overall height.
Windy or Coastal Regions:
Roof Design: Stronger, wind-resistant roof structures may increase height.
Elevation Concerns: Houses may be elevated for flood protection, impacting height.
Materials: Durable materials for coastal weather may add to the building’s height.
Mountainous or Hilly Areas:
Slope Adaptations: Houses may be built higher to accommodate sloped terrain.
Foundation Stability: Deeper foundations may be necessary for stability on slopes.
Aesthetic Considerations: Rooflines may follow the natural contours, affecting height.
Urban Areas:

Zoning Regulations: Height restrictions in urban areas may limit building height.
Space Optimization: Efficient use of space may lead to taller structures.
Aesthetic Norms: Architectural styles in cities may influence building heights.
Earthquake-Prone Regions:
Foundation Strength: Deeper and reinforced foundations for seismic stability may increase height.
Building Materials: Use of earthquake-resistant materials can affect overall building height.
Design Considerations: Architects may opt for lower profiles or wider bases for stability.
Local Regulations: Building codes in seismic zones may mandate specific height-to-width ratios.
Structural Reinforcements: Bracing, shear walls, or other reinforcements may impact height.
High Earthquake Risk Zones (e.g., Ring of Fire, Himalayan Belt):

Foundation Strength: Deeper and reinforced foundations for seismic stability may increase height.
Building Materials: In earthquake-prone areas, construction materials like reinforced concrete and steel frames provide strength and flexibility to withstand seismic forces. Retrofitting techniques, timber with steel bracing, and advanced materials like fiber-reinforced polymers enhance earthquake resistance.
Lightweight materials and proper foundation design further improve structural integrity, ensuring buildings can withstand seismic events safely.
Design Considerations: Architects may opt for lower profiles or wider bases for stability.
Local Regulations: Building codes in seismic zones may mandate specific height-to-width ratios.
Structural Reinforcements: Bracing, shear walls, or other reinforcements may impact height.
The above considerations are essential for safety in earthquake-prone regions like the Pacific Ring of Fire and the Himalayan Belt. These measures enhance the resilience of buildings against seismic activity worldwide.
Read this blog: How Tall Is A Dining Room Table
How to Measure the Height of a two Storey Building?
Measuring the height of a two-storey building involves several steps:
Exterior Measurement: Stand outside the building and use a tape measure to measure from the ground to the top of the roof ridge or peak. This provides the overall height from the exterior.
Interior Measurement: Measure from the ground floor to the ceiling inside the building. For a standard two-storey building, double this measurement to determine the interior height.
Foundation Depth: Measure the depth of the foundation from ground level to the base of the building. This is important for assessing the total vertical dimension.
Roof Pitch: Try to ascertain the roof pitch, as it impacts the overall building height. Measure how much the roof rises vertically for every foot horizontally to calculate accurately.
Combine Measurements: To find the total height from ground to roof, add the exterior measurement (roof height) to the foundation depth. This calculation provides a comprehensive measure of the building’s vertical extent. This accounts for the full vertical extent of the building.
Factors Influencing Height of TWO Storey House
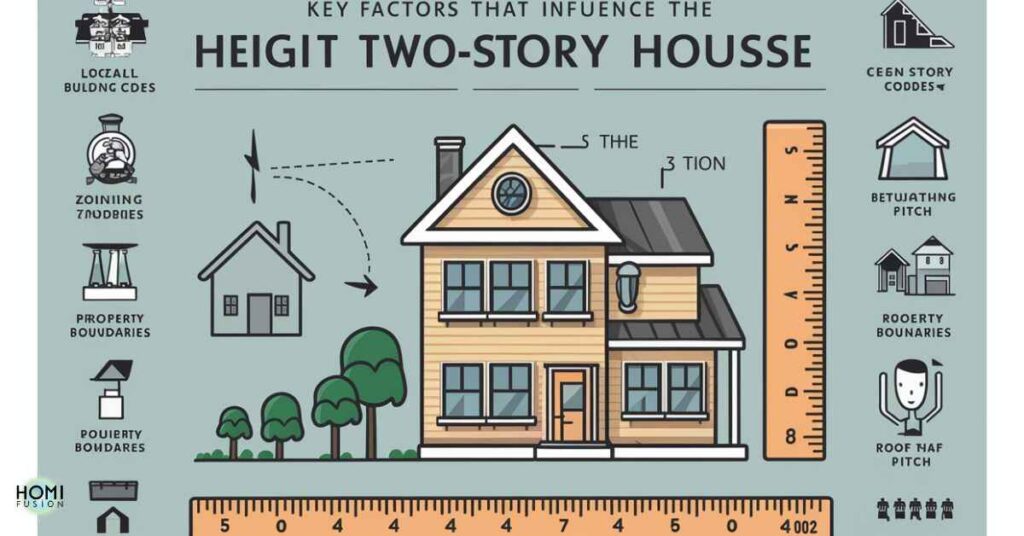
Planning Regulations
Planning regulations in a specific area can dictate the maximum allowable height of buildings. These regulations ensure that structures fit within the overall urban or suburban landscape and comply with safety standards.
Land Cost
The cost of land can influence the height of a two-storey house. Areas where land is expensive, homeowners may opt for taller buildings to maximize living space while minimizing the land footprint.
Lifestyle Choices
Individual lifestyle choices play a role in determining the height of a two-storey house. Some may prefer higher ceilings or additional floors for specific functions like entertainment areas or home offices.
Architectural Style:
Different architectural styles may have varying heights. For example, a Victorian-style house may have higher ceilings and rooflines compared to a modern minimalist design.
Building Codes and Regulations:
Local building codes and regulations set standards for structural safety and may specify minimum and maximum building heights.
Economic Factors
Economic considerations, including construction costs and resale value, can impact the decision to build two-storey house of a certain height.
Foundation Height
The depth and design of the foundation influence the overall height of a two-storey house. Deeper foundations may be necessary for stability, especially in areas prone to seismic activity.
Ceiling Height:
The desired ceiling height also affects overall building height. Higher ceilings can make spaces feel more open and spacious but contribute to taller structures.
Sustainability
Sustainability goals can influence building height. Green building practices may involve features like solar panels or green roofs, which can affect the overall vertical dimension.
Location
The location of the property, such as urban or rural areas, can impact building height due to zoning regulations and aesthetic considerations.
Roof Pitch
The pitch of the roof affects the overall height. Steeper pitches add vertical space, while flatter roofs reduce overall building height.
The Thickness of the Floor
The thickness of the floor structure between levels can impact overall height, especially in buildings with multiple stories.
The Height of the Attic Ceiling
If the house includes an attic space, the height of the attic ceiling contributes to the overall vertical dimension of the building.
The Height of the First Floor
The height of the first floor sets the baseline for subsequent floors and affects the overall height of the two-storey house.
The Height of the Second Floor
The height of the second floor, including ceiling height and floor structure, completes the vertical dimension of the two-storey house.
What Size Ladder Do I Need for Maintenance Tasks on a Two-Storey House?

To safely perform maintenance tasks on a two-storey house, you generally need a ladder that extends at least 20 feet. This ensures you can reach the eaves, gutters and other areas safely.
How tall is a one storey house?
A one-storey house typically has a ceiling height ranging from 8 to 10 feet. A one-story house usually ranges from 10 to 12 feet tall, encompassing the roof structure. This measurement represents the total height from the ground to the roofline.
How tall is a three-storey house?
The approximate height of a three-storey house:
Ceiling Height: A standard ceiling height for each floor is typically 8 to 10 feet.
Number of Floors: Multiply the ceiling height by the number of floors (3 floors for a three-storey house). Ceiling Height x Number of Floors
8 feet x 3 floors = 24 feet
10 feet x 3 floors = 30 feet
A three-storey house typically stands between 24 to 30 feet tall from the ground to the roofline. This range varies based on the chosen ceiling height for each floor.
Also read: What Is In-House Financing?
Advantages And Disadvantages

Advantages
Spaciousness: Two-storey houses offer increased living space per land area, making them suitable for larger families. They are also favored by those who frequently entertain guests due to their spacious layout.
Separation of Spaces: Two-storey houses provide separate levels for living, sleeping, and recreation, enhancing privacy. This layout also improves noise isolation, resulting in a more comfortable living atmosphere.
Views and Ventilation: Higher floors can offer better views and improved ventilation, especially in areas with scenic surroundings or pleasant climates.
Customization: Two-storey homes offer architectural flexibility, allowing homeowners to customize floor plans and room layouts. This customization aligns with their specific needs and preferences for living spaces.
Land Utilization: High land costs in certain areas make vertical construction beneficial. A two-storey design optimizes land use, maximizing available space efficiently.
Disadvantages
Accessibility: Stairs pose challenges for those with mobility issues, young children, or elderly family members. Additional safety measures or modifications may be necessary to address these concerns.
Costs: Constructing a two-storey house often incurs higher costs due to added materials and labor. Structural elements such as stairs contribute to these increased expenses.
Maintenance: Maintaining a two-storey house can be more demanding, especially for tasks like window and gutter cleaning. Areas such as roofs may also require regular upkeep, adding to the maintenance challenges.
Heating and Cooling: Two-storey houses may necessitate distinct heating and cooling systems per floor. Inefficient designs can result in increased energy expenses.
Resale Value: Two-storey houses have advantages but might appeal to a smaller market than single-storey homes. This can influence resale value based on market trends and buyer preferences.
Risk of Damage in Earthquakes: Taller buildings are more susceptible to structural damage during earthquakes, posing a safety risk.
Frequently asked questions
What is the average height of a 2-floor house?
The average height of a two-floor house ranges from 18 to 25 feet. This range considers factors such as ceiling height and roof design.
How tall is a two storey house UK?
In the UK, a two storey house typically stands at an average height of 20 to 25 feet. This measurement includes both floors and the roof structure.
How tall is a 3-storey house?
A three-storey house generally ranges from 24 to 30 feet in height. This calculation assumes an average ceiling height of 8 to 10 feet per floor.
Conclusion
A two-storey house typically stands around 18 to 25 feet tall. This height varies based on factors like ceiling height, roof design, and architectural style. Overall, a two storey house provides ample vertical space while remaining compact and functional.
Considering factors such as building codes, economic factors, and customization options influences the height. It’s important to balance aesthetics, functionality, and safety when determining the height of a two storey house.